Joint Pain And Intestinal Bacteria
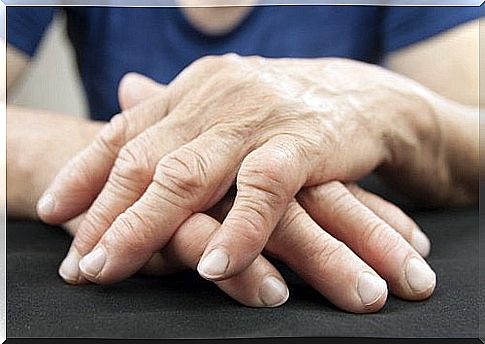
Rheumatoid arthritis is caused by damaged cartilage, causing inflammation and pain. Although experts have discovered several factors that trigger this disease, its direct cause is still unknown. A group of researchers focused on a new potential enemy. Thus they discovered the connection between joint pain and intestinal bacteria.
Recent studies have shown that intestinal bacteria can cause joint pain, including pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis. These are correlated with diseases that prevent the proper functioning of the immune system, leading to many chronic problems.
The link between joint pain and intestinal bacteria
In a 2013 study, Dr. José Scher, a rheumatologist at New York University, found that patients with rheumatoid arthritis were more likely to have a bacterium called Prevotella copri in their gut .
In another study published in October of that year, Scher found that people with psoriatic arthritis have lower levels of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
These studies are part of an effort by scientists around the world to understand and explain the role that the microbiome (all microbes in the gastrointestinal tract) has on general health.
The intestinal flora is composed of over 1,000 species of bacteria that weigh together between 900 g and 2.5 kg. In recent years, researchers have tried to show that these microorganisms are closely related to human health. Some of them cause various diseases, while others protect the body.
Bacteria in the gut affect the immune system
Veena Taneja, an immunologist at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, says: “With each study, it is becoming increasingly clear that these microbes can damage the immune system, causing disease outside the gut. The connection between joint pain and intestinal bacteria is obvious. “
The researchers were surprised to find that intestinal bacteria influence the immune system more than they thought.
Cases of autoimmune diseases have multiplied in recent decades. Many experts are convinced that the modern lifestyle and the changes it causes in the microbiome are at least partly responsible for these statistics.
Prevotella bacteria could cause joint pain
These microbes affect the health of the intestines, the space where two thirds of the cells of the immune system are located. During digestion, the gastrointestinal tract faces a constant flow of foreign microbes. They accompany ingested food.
To perform their functions, the intestines have developed a vast immune system that extends to other organs. Immune cells present in the intestines have the ability to activate inflammatory cells throughout the body, including those in the joints.
According to specialist José Scher, the bacterium called Prevotella copri can cause an immune reaction that later spreads to other tissues, causing joint pain. Another theory holds that beneficial microbes are lost, leading to a weakened immune system.
The latest theory is one of the most widely supported, as a study found that patients with high levels of Prevotella copri have low levels of Bacteroides fragilis , a beneficial bacterium that strengthens the immune system.
The results of these studies have encouraged further research to create strategies for using bacteria as treatments for autoimmune diseases.
Doctors already recommend probiotics (good bacteria) to restore the intestinal flora and treat other health problems, such as acne, insomnia and other intestinal conditions.