What Is The Body’s Immune Response?
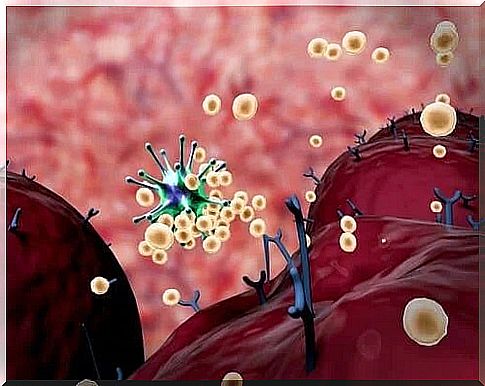
The immune response is an essential mechanism of the human body that we use to protect ourselves from external agents that can be harmful to health. It is made up of different processes in which several types of cells are involved. In this article, we will tell you everything you need to know about the body’s immune response.
What is the body’s immune response?
The immune response is the set of processes that the body goes through to recognize and eliminate external agents that it perceives as harmful. These processes are based on the recognition of foreign substances, also known as antigens.
Antigens are usually found on the surface of viruses, bacteria and fungi. They are also found in inert substances, such as chemicals. Other materials or toxins can also be antigens.
People have defined two different types of immunity. In the following, we will tell you what it is about.
Innate immunity
- Barriers can be physical, such as skin that prevents chemicals from entering the body. There are many chemical barriers present in the human body (for example, nasal secretions, tears, saliva or vaginal discharge). These substances have characteristics that make it difficult for viruses or bacteria to survive. We can mention the pH of vaginal discharge as an example, because most pathogens cannot survive in these fluids.
- Cellular mechanisms include the complementary system, the inflammatory mechanism, and phagocytes. The basis of all three mechanisms are the substances present in the blood, which circulate continuously in the vessels. These systems are active for the elimination of any foreign agent that enters the body.
This is the second type of immune response. Unlike the innate response, we are not born with a specific developed immunity. It is shaped as the body comes in contact with various antigens. It becomes faster and more efficient in eliminating pathogens.
The tissue responsible for this type of immunity is lymphoid tissue, made up of organs such as the spleen or thymus and lymphatic vessels. This tissue hosts the production of lymphocytes, the cells responsible for generating the immune response.
Specific parts of the immune system, called epitopes, recognize invasive antigens. Innate immunity activates faster, but is less effective. Specific immunity is slower, but much more effective.
A lymphocyte will recognize the epitope of an antigen. You may not know this, but lymphocytes are responsible for producing substances called antibodies, which will be responsible for eliminating the pathogen. In addition, lymphocytes will activate more lymphocytes, which will travel to the site of infection to help eliminate antigens. This is the specific primary immune response.
In addition to the primary immune response, there is also a production of memory lymphocytes. These memory lymphocytes will cause specific immunity when they come in contact with the same type of antigen. In fact, they activate faster to remove the harmful agent. This process is known as a secondary immune response.
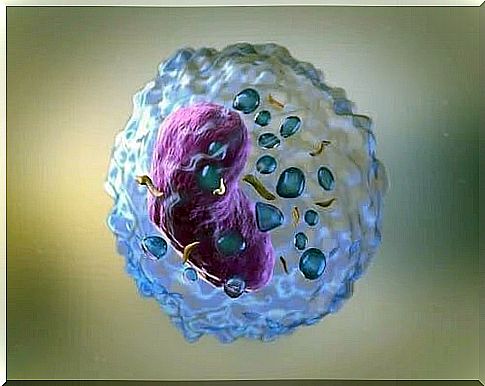
Passive and active immunity
Sometimes, specific antibodies are already circulating in the body without being in contact with antigens. This can only happen in two situations:
- In newborns, thanks to the antibodies that the mother transmits to the baby during pregnancy.
- In vaccinated individuals, because vaccines may contain antibodies or fragments of the pathogen that trigger the production of memory lymphocytes without actually causing the disease.









